Environmental Collapse: What Happens When Biodiversity Disappears
The foundation of life: understand biodiversity’s role
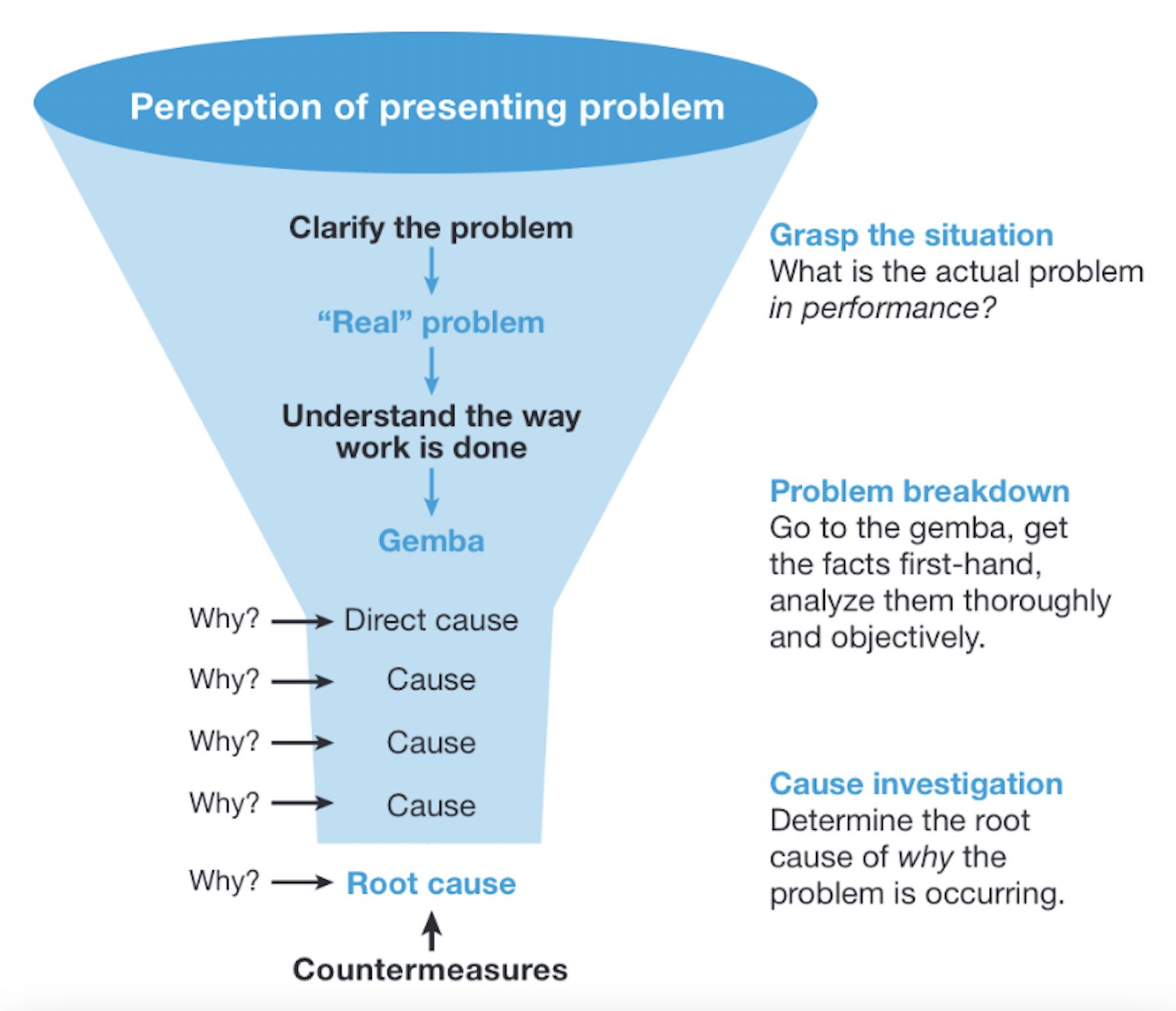
Biodiversity represent the incredible variety of life forms inhabit earth, from microscopic bacteria to tower redwood trees. This biological diversity create complex networks where each species play a crucial role in maintain ecosystem stability. When we imagine a world with dramatically reduce biodiversity, we’re fundamentally contemplated the collapse of these intricate support systems that have evolved over millions of years.
The biosphere operate like a vast, interconnect machine where every component serve a purpose. Plants convert sunlight into energy, decomposers break down organic matter, predators control population levels, and pollinators ensure plant reproduction. Remove enough pieces from this biological puzzle, and the entire system begin to unravel.
Ecosystem services under threat
A world with limited biodiversity would struggle to provide the essential services that presently sustain life on earth. These ecosystem services include water purification, soil formation, climate regulation, and nutrient cycling. Without diverse plant communities, soil erosion would accelerate dramatically as root systems that ordinarily bind earth unitedly disappear.
Water quality would deteriorate apace without wetland plants that filter pollutants and diverse aquatic communities that maintain chemical balance. Rivers and lakes would become progressively contaminate, make clean water scarce for both human consumption and agricultural use. The natural water cycle itself would become disrupt as forests, which play crucial roles in precipitation patterns, vanish from the landscape.
Air quality would suffer hugely in a biodiversity poor world. Trees and plants presently absorb billions of tons of carbon dioxide while release oxygen. With fewer species perform photosynthesis, atmospheric carbon levels would skyrocket, accelerate climate change and reduce oxygen availability for all aerobic life forms.
Agricultural catastrophe and food security
Modern agriculture depend intemperately on biodiversity, though this relationship oftentimes goes unnoticed. Pollinators like bees, butterflies, and birds enable the reproduction of countless food crops. Without diverse pollinator populations, agricultural yields would plummet, create widespread food shortages.
Soil health rely on complex communities of microorganisms, insects, and other small creatures that break down organic matter and cycle nutrients. In a world with reduced biodiversity, soil would become progressively deplete and unable to support robust crop growth. Farmers would face mount challenges as natural pest control disappear, force greater reliance on chemical interventions that further damage remain ecosystems.
Genetic diversity within crop species provide resilience against diseases and change environmental conditions. A biosphere lack diversity would leave humanity vulnerable to catastrophic crop failures, as uniform plant varieties would be susceptible to the same threats simultaneously.
Climate regulation breakdown
Biodiversity play a fundamental role in regulate earth’s climate through various mechanisms. Forests absorb carbon dioxide and influence local weather patterns through evapotranspiration. Ocean ecosystem help regulate temperature through complex food webs that affect carbon cycling in marine environments.
Without diverse ecosystems, climate regulation would become progressively unstable. Temperature fluctuations would become more extreme, weather patterns more unpredictable, and natural disasters more frequent and severe. The planet’s ability to buffer against climate change would diminish importantly, accelerate environmental degradation.
Coastal protection would deteriorate as mangrove forests, coral reefs, and other diverse marine ecosystems that presently shield shorelines from storms and erosion disappear. Rise sea levels would pose greater threats to human settlements as natural barriers vanish.
Disease and health implications
Biodiversity loss would create serious public health consequences of multiple pathways. Many medicines derive from natural compounds find in plants, animals, and microorganisms. A world with limited biological diversity would offer fewer opportunities for medical discoveries and treatments for diseases.
Disease outbreaks would become more frequent and severe without diverse ecosystems to regulate pathogen populations. Presently, biodiversity help control disease vectors and provide natural checks on harmful organisms. Reduced species diversity would eliminate these natural controls, potentially lead to pandemic conditions.
Mental and physical health would suffer as natural environments become progressively barren and polluted. The psychological benefits of interact with diverse natural settings would disappear, contribute to widespread mental health challenges in human populations.

Source: studylib.net
Economic collapse and resource scarcity
The economic implications of gravely reduce biodiversity would be staggering. Industries dependent on natural resources would face shortages and increase costs. Tourism base on natural attractions would collapse as ecosystems lose their appeal and functionality.
Fishing industries would struggle as marine food webs collapse, lead to widespread unemployment in coastal communities. Forestry would become unsustainable as simplified forest ecosystems prove unable to regenerate efficaciously.
The cost of replace ecosystem services with human engineer solutions would be prohibitive. Water treatment facilities would need massive expansion to handle purification tasks presently perform by wetlands and riparian forests. Artificial pollination would require enormous labor investments to replace natural pollinators.
Social and cultural devastation
Human societies would face unprecedented challenges in a world lack biodiversity. Indigenous communities whose cultures are closely connected to diverse natural environments would lose essential elements of their identity and traditional knowledge systems.
Food security issues would probable lead to social unrest and conflict as communities compete for progressively scarce resources. Migration patterns would shift dramatically as environmental refugees flee degrade landscapes in search of habitable areas.
Educational opportunities would diminish as natural laboratories for learn about biology, ecology, and environmental science disappear. Future generations would grow up disconnected from the natural world, lack understanding of ecological principles that erstwhile guide sustainable living practices.
Technological limitations and innovation loss
Biodiversity serve as inspiration for countless technological innovations through biomimicry. Velcro was inspired by burr seeds, airplane wing design mimics bird flight, and medical devices copy natural mechanisms. A world with limited biological diversity would offer fewer models for technological advancement.

Source: intalek.com
Scientific research would suffer as natural laboratories disappear. Understanding of biological processes, evolutionary mechanisms, and ecological relationships would become progressively limited, hamper progress in fields range from medicine to engineering.
The loss of genetic resources would eliminate potential solutions to future challenges. Species that might hold keys to address climate change, develop new materials, or treat diseases would vanish before their potential could be realized.
Cascade effects and tipping points
Environmental degradation in a biodiversity poor world would accelerate through cascade effects. The loss of one species oftentimes trigger the decline of others, create downward spirals that become progressively difficult to reverse.
Ecosystem tipping points would be reach more rapidly as simplified biological communities lack the resilience to recover from disturbances. Once these thresholds are cross, ecosystems would shift to alternative states that might be unable to support complex life forms.
The interconnected nature of global ecosystems mean that collapse in one region would trigger problems elsewhere. Ocean current changes, atmospheric circulation shifts, and alter precipitation patterns would spread environmental damage across the planet.
Hope through understanding
While the scenarios describe paint a dire picture, understand these potential consequences emphasize the critical importance of biodiversity conservation. Current efforts to protect species and ecosystems take on greater urgency when view through the lens of these possible futures.
Every species preserve, every habitat protects, and every conservation success story represent a step out from the environmental catastrophe that would result from biodiversity loss. The complexity and beauty of our current biosphere, with its millions of interconnected species, provide the foundation for all life on earth.
Recognize biodiversity’s value help inform decisions about land use, resource management, and environmental policy. The alternative a simplified world struggle to maintain basic life support systems serve as powerful motivation for protecting the incredible diversity of life that presently surround us.
MORE FROM techitio.com